08 | Governance
Risk management
Risk is inherent in the business activities of Hafnia, and managing them is critical for ensuring long-term success. Hafnia’s overall risk management program focuses on the unpredictability of financial markets and seeks to minimise potential adverse effects on Hafnia’s financial performance, to create sustainable value for our customers, employees, shareholders and the community. Hafnia’s results are dependent on the market for worldwide transportation of refined oil products. With that, the Company is exposed to a variety of financial risks: market risk (including price risk and currency risk), interest rate risk, credit risk, liquidity risk and capital risk.
The most significant risks are set out in the 2020 prospectus issued in April 2020. That document and other information on risks are available on the Company’s website at www.hafniabw.com.
Hafnia Limited and its activities are primarily governed by the Bermuda Companies Act, its Memorandum of Association, and its by-laws.
Certain aspects of Hafnia’s activities are governed by Norwegian law pursuant. In particular, the Norwegian Securities Trading Act and the Norwegian Stock Exchange Regulations will generally apply.

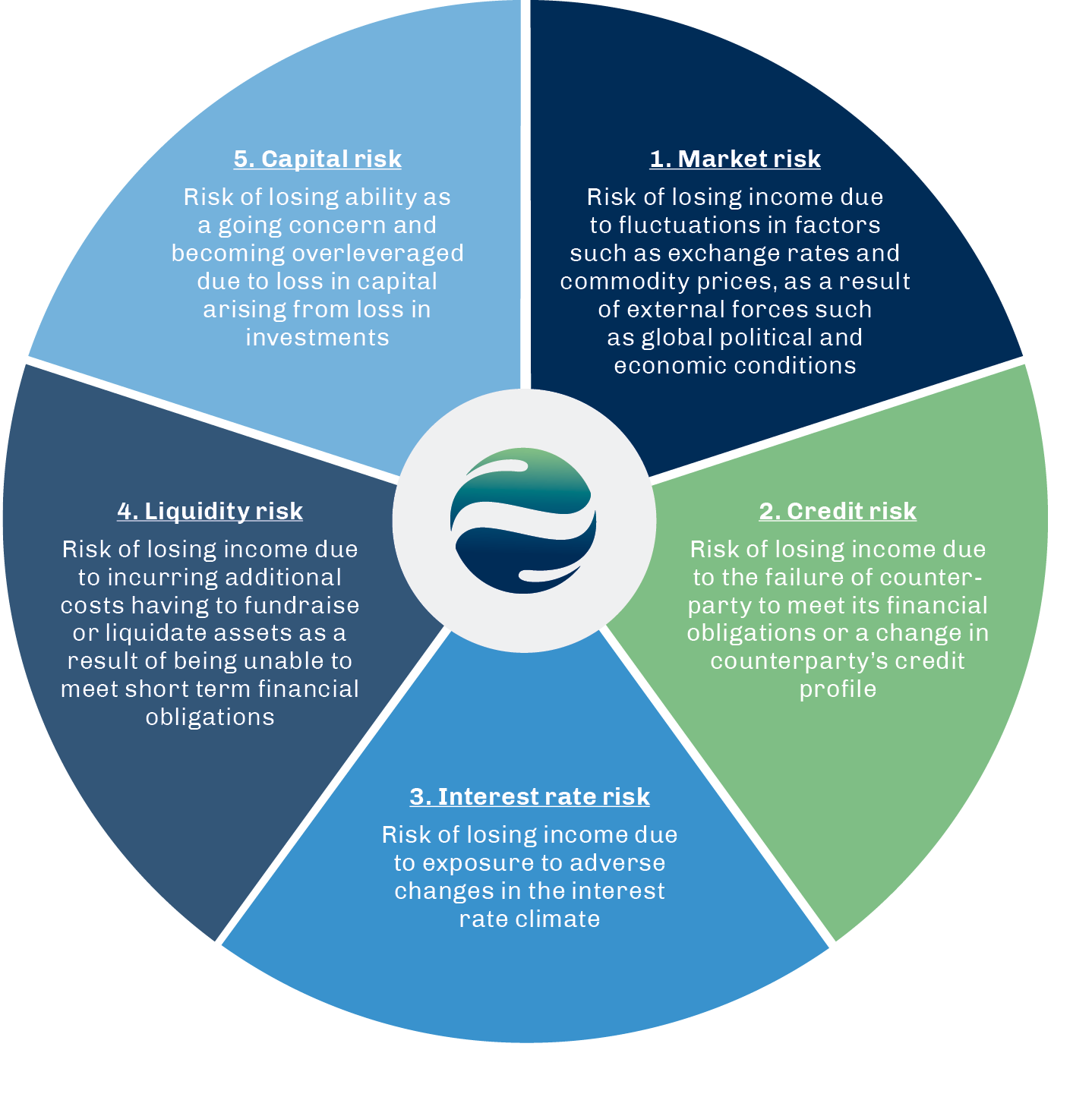
Market risks
The shipping industry can be subject to significant fluctuations. Being in the product tanker market, Hafnia is exposed to the risk of global weak oil consumption and demand, which are affected by global political and economic conditions.
Under time charter or bareboat charter, the charterer is responsible for bunker fuel costs, which historically has been the most significant expense. As a result, Hafnia is also exposed to price volatility of bunker fuel.
How is it managed?
Hafnia’s chartering strategy is to secure fixed-income employment for a portion of its fleet, which is employed under various chartering arrangements including time charters and spot voyage charters. With this strategy, Hafnia is also able to reduce exposure to fuel price fluctuations.
Credit risks
Hafnia’s credit risk arises from counterparty and issuer credit risks, primarily attributable to trade and other receivables and cash and cash equivalents. The carrying carrying value represents the maximum exposure value of each financial asset on the balance sheet.
How is it managed?
Hafnia performs a KYC check for all new customers and keep the knowledge of our customers updated, in addition Hafnia performes creditworthiness analysis of customers and has an authorisation matrix outlining the authority to enter in to contracts with customers.
Interest rate risks
Hafnia is exposed to adverse changes in the interest rate environment, primarily attributable to interest-bearing financial liabilities in the form of bank borrowings at variable interest rates.
How is it managed?
Hafnia uses financial instruments such as interest rate caps and interest rate swaps to hedge against adverse interest rate fluctuations.
Liquidity risks
Hafnia is exposed to the inability to meet short term liquidity requirements, due to unpredictable earnings to additional costs through fundraising or asset liquidation.
How is it managed?
To meet operating, capital expenditure and potential short-term liquidity needs, Hafnia maintains sufficient cash for its daily operations in short-term cash deposits with banks and has access to unutilised portions of revolving facilities provided by financial institutions.
Capital risks
Hafnia is exposed to potential loss in investments or capital, potentially leading to Company becoming increasingly leveraged.
How is it managed?
To safeguard the ability to continue as a going concern and maintain an optimal capital structure to maximise value for shareholders, Hafnia may adjust the amount paid in dividends, obtain new loans or sell assets to reduce debt.